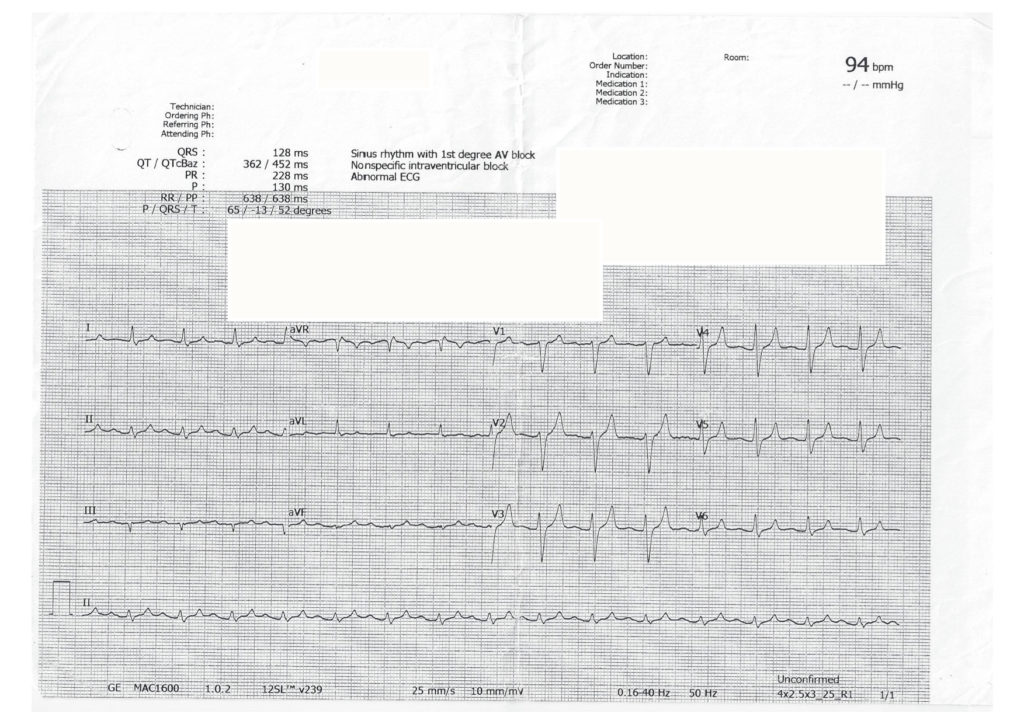
Key Features
- Sinus Rhythm
- Wide QRS
- Peaked T waves
- Flattened p waves
Interpretation = Hyperkalaemia
… 20 minutes post calcium gluconate:
- QRS narrows
- T waves decrease in amplitude
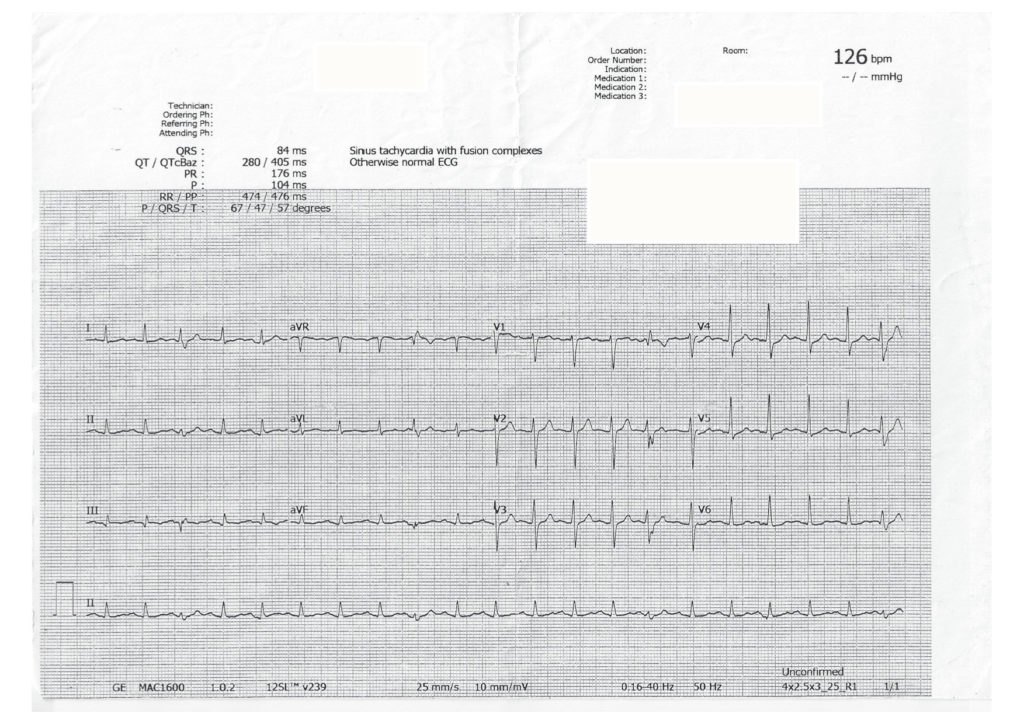
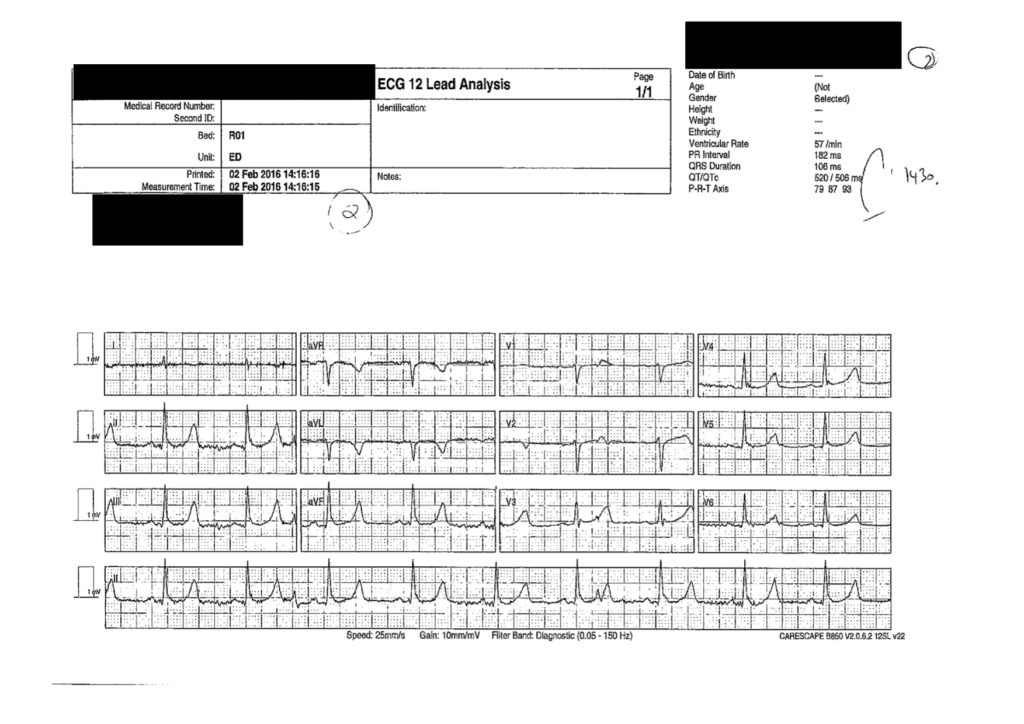
40 year old lady found unconscious in bed. Seen completely well 2 hours earlier by husband.
Key Features
- Irregular tachycardia ?AF
- Wide complex
- Prominent terminal R wave in aVR (Right axis deviation of the terminal QRS)
Interpretation
- Given history of sudden deterioration in consciousness from well state and these ECG findings – Sodium Channel Blockade from overdose
Sodium Channel Blocking Drugs include:
- TCA’s (tricyclic antidepressants): Amitriptyline, Desimipramine, Dothiepin, Imipramine, Nortripytline
- Class 1A anti-arrhythmics: Disopyramide, Procainamide, Quinidine
- Class 1C anti-arrhythmics: Flecanide
- Local Anaesthetics: Bupivacaine, Cocaine, Ropivacaine
Antimalarials: Hydroxychloroquine/Chloroquine, Quinine - Other: Phenothiazines (Thioridazine), Amantadine, Carbamazepine, Chloroquine, Diltiazem, Diphenhydramine, Propoxyphene/Dextropropoxyphene, Propanolol
Source: Toxicology Handbook, 3rd edition, Murray et al
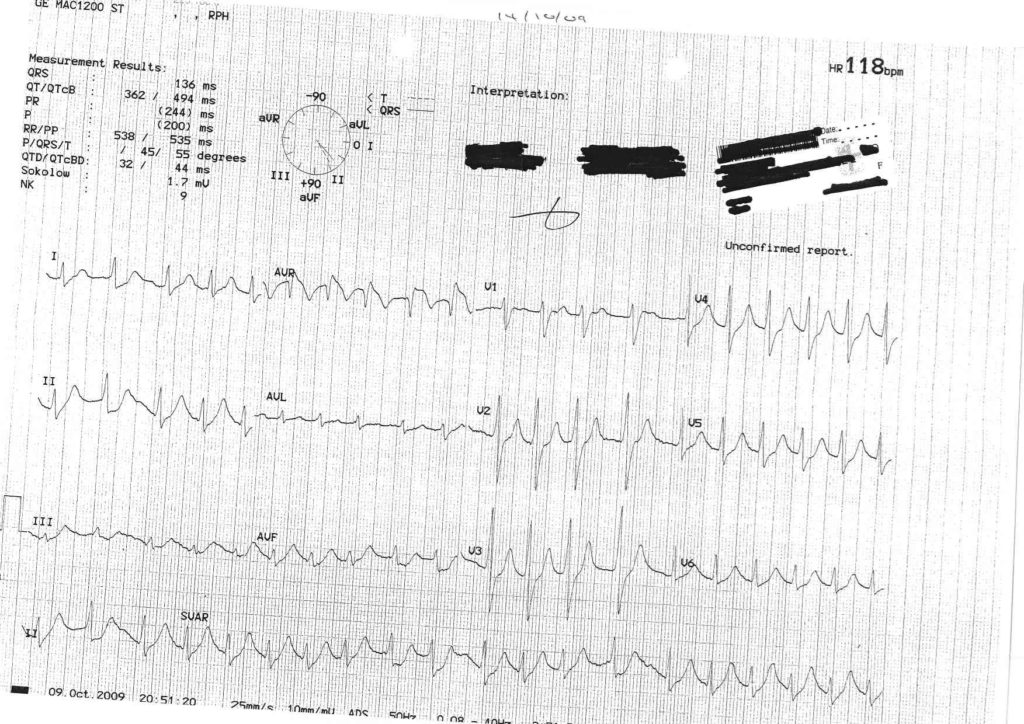
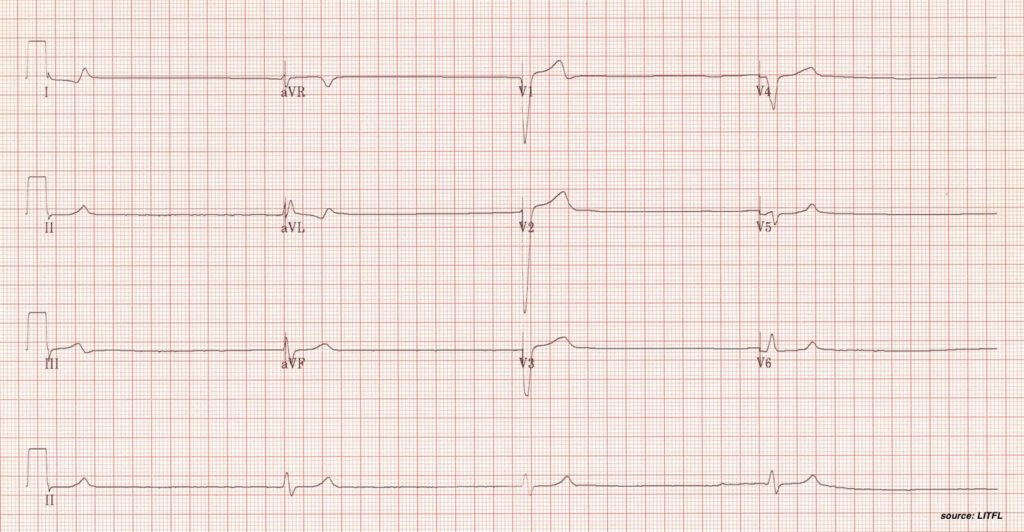
Key Features
- Regular bradycardia
- Wide complex
- Baseline artefact (shivering)
- Osborne J waves (prominent notching at end of QRS)
Further history
- 80y.o lady fell over on way back to toilet in middle of night. Unable to get up and found on floor after 24hrs.
Interpretation
Hypothermia
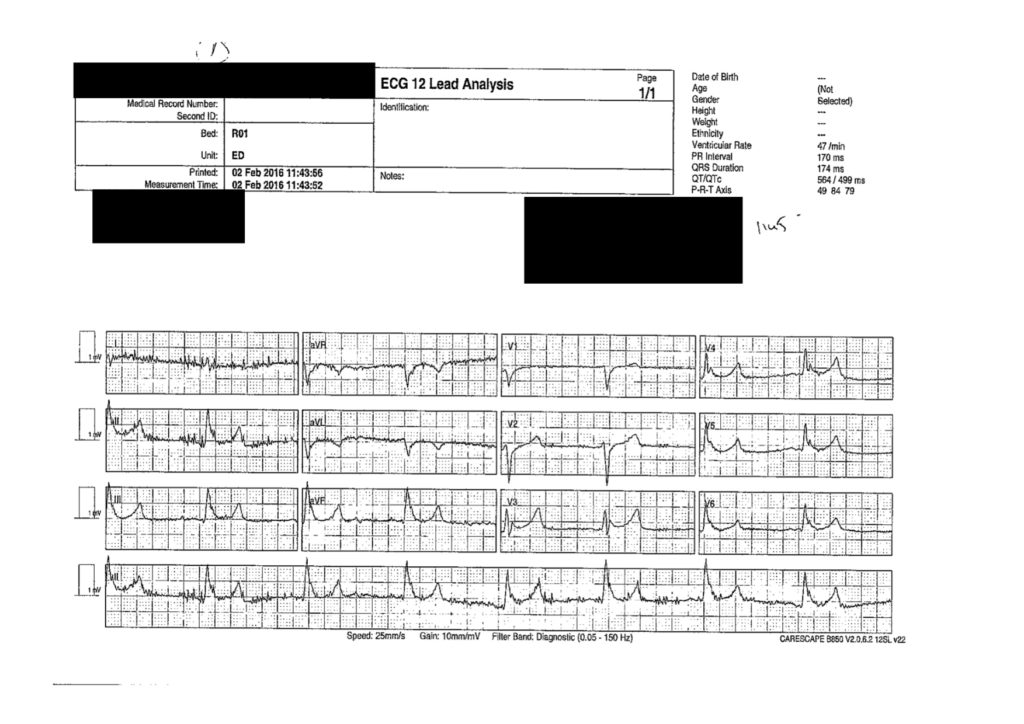
…. After rewarming 2 degrees
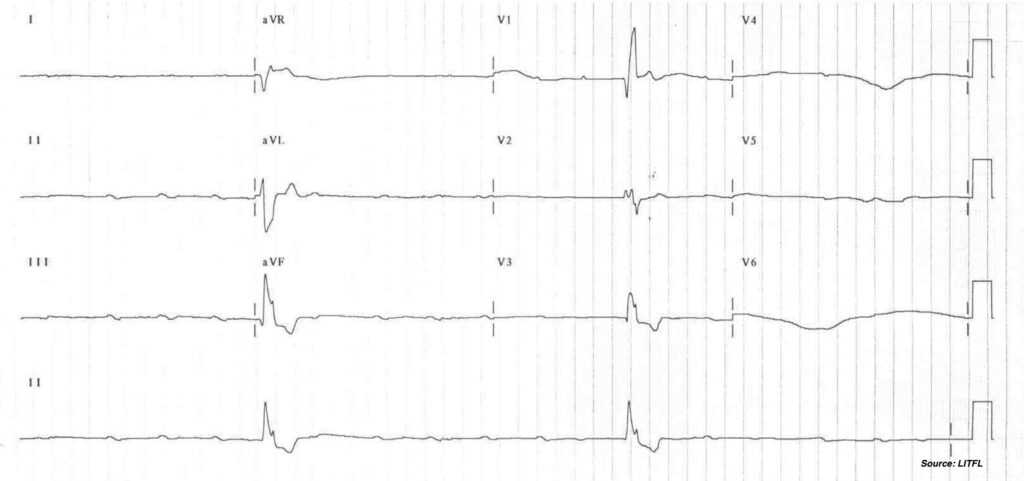
Key Features
- Very slow rate
- Wide
- and…
- ECG 4(a)
- Near total absence of atrial activity
- ECG (b)
- Regular atrial activity without relationship to ventricular activity
Interpretation = Ventricular Escape Rhythms
- 4(a) Due to sinus arrest
- 4(b) Due to complete heart block
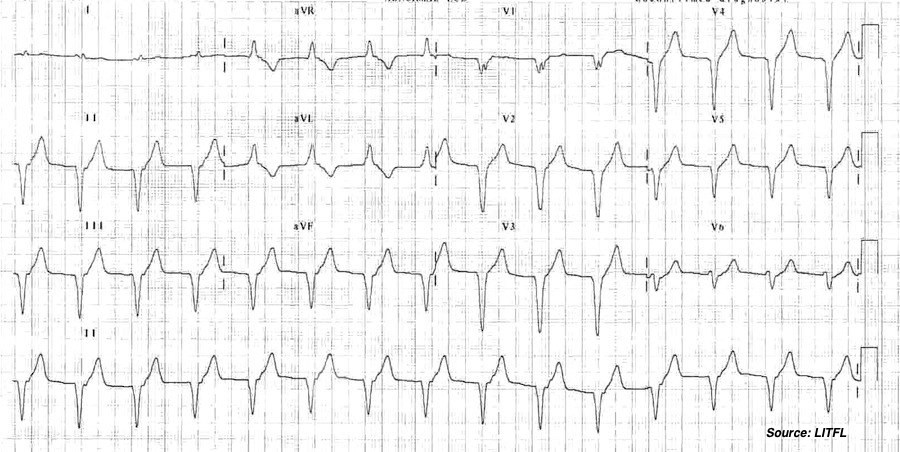
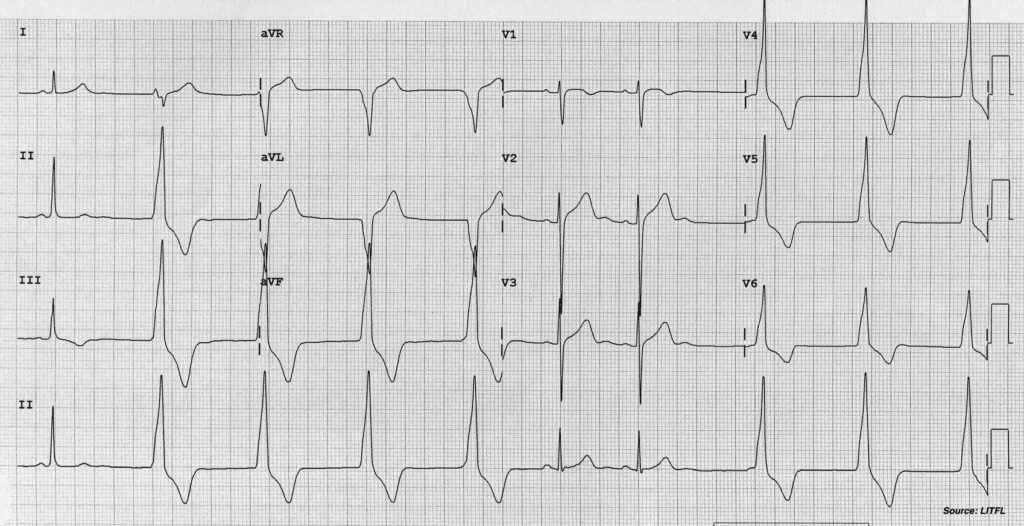
Key Features
- Wide regular rhythms
- Unusually “normal” rate
- Faster than usual ventricular escape rhythms
- Slower than VT
- Unusually “normal” rate
- Nil other features to suggest a Tox/Metabolic cause
Interpretation – Accelerated IdioVentricular Rhythm (AIVR) due to
- 5(a) MI post reperfusion
- 5(b) Athlete’s heart (sinus beats with intermittent AIVR)
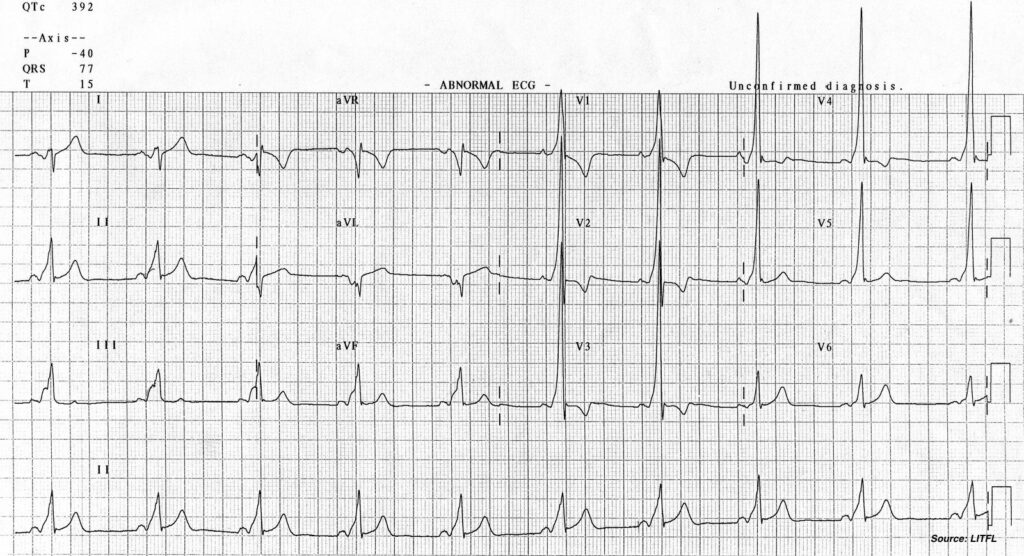
Key features
- Wide QRS
- Short PR
- Delta waves
Interpretation: Accessory Pathway – Wolf Parkinson White (WPW)
Key causes of a Wide QRS
- Bundle Branch Block
- Accessory Pathway
- Ventricular rhythm
- Ventricular escape rhythm
- AIVR – Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Toxicology/Metabolic (Cellular poisoning
- Hyperkalaemia
- Sodium Channel Blockade
- Hypothermia
Key Diagnostic Clues
- History:
- Toxicological cause? Hypothermia? Reasons for hyperkalaemia?
- ECG findings
- Heart rate:
- Slow – think ventricular escape rhythms; think hypothermia if history/temp supports
- Very fast – think VT
- QRS Morphology
- Features/appearance of RBBB or LBBB?
- Other ECG abnormalities
- Peaked T waves, Short PR/delta waves, Osborne J waves, Terminal R wave in aVR
- Heart rate:
